What's SOLID?
SOLID is design principles that enable us to manage, maintain and scale software design problems .
What's 'SOLID' stand for?
"SOLID" is actually an acronym in software development that represents a set of five design principles to create more maintainable and scalable software
- S - Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
- O - Open/Closed Principle (OCP)
- L - Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
- I - Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
- D - Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
In this article we talk about 'S - Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)' to help you understand why you should use these principles in your code and how to implement
What's Single Responsibility Principle ?
S => Definition By Robert Martin
- Every software module should have only one reason to change.
- Everything in that Interface/Class should be related to a single purpose
Example Description:
Consider the example below where we implement CRUD operations for Application. Additionally, we incorporate the "S" principles, which stand for [Single Responsibility Principle]. For instance, we send notifications such as SMS and Email whenever a create operation is performed in the application .
Example:
- It is not preferred to create a 'SendEmail' operation in the application service because the 'S' in SOLID signifies that you should only create operations that are specifically related to the application service.
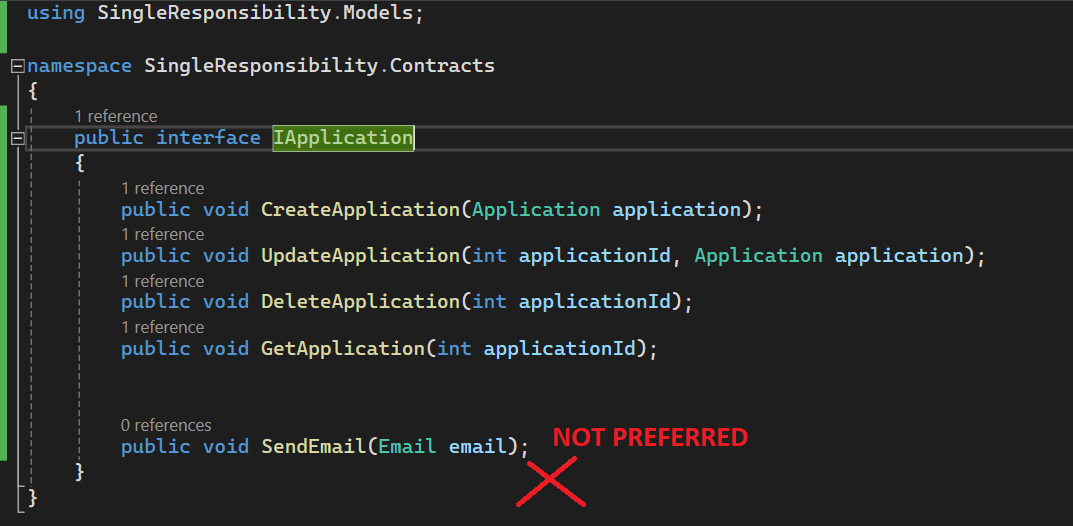
- Preferably, create an interface for the application service and another interface for the notification service, ensuring a clear separation of concerns
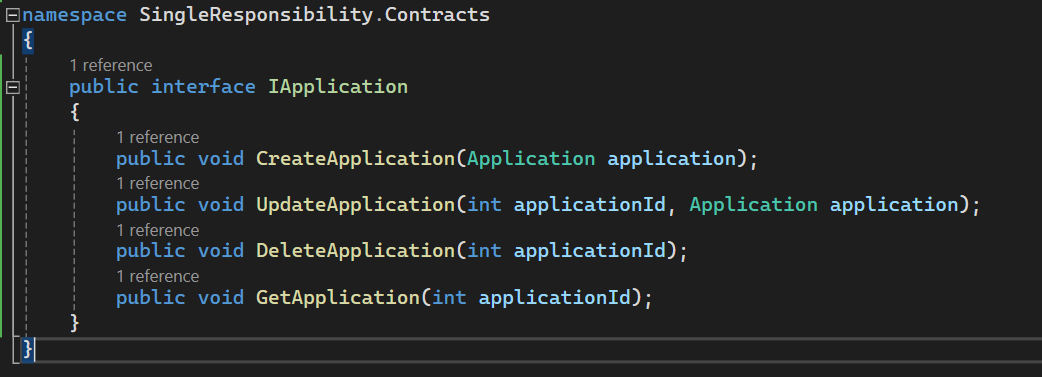
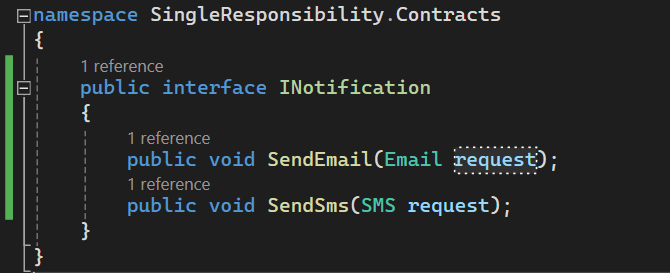
Code:
Service not implemented, i want to discuss principle .
public interface IApplication
{
public void CreateApplication(Application application);
public void UpdateApplication(int applicationId, Application application);
public void DeleteApplication(int applicationId);
public void GetApplication(int applicationId);
}
public class Application : IApplication
{
public void CreateApplication(Models.Application application)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void DeleteApplication(int applicationId)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void GetApplication(int applicationId)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void UpdateApplication(int applicationId, Models.Application application)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
public interface INotification
{
public void SendEmail(Email request);
public void SendSms(SMS request);
}
public class Notification : INotification
{
public void SendEmail(Email request)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void SendSms(SMS request)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}